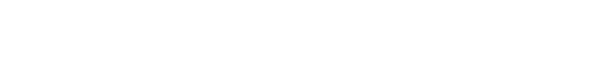Connecting Devices to the S7-1200 PLC Outputs
The time has come to transmit a signal from the Siemens S7-1200 PLC to actuators.
Remember, not everything can be directly connected to the controller, for example, you cannot directly connect an induction motor or solenoid valve!
Read this Siemens S7-1200 PLC tutorial to find out more about digital outputs of this PLC.
What Can You Connect to PLC Outputs?

Below is a list of example devices that you can connect directly to the PLC controller.
REMEMBER! Always pay attention to the current capacity of the contacts.
| Device Type | Description | Example Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal light | Output device used to visually signal the status of a machine or process | Turck TL503AOSKQ light tower |  |
| Contactor | Switching device used to control electric motors and other heavy loads | Schneider Electric LC1K0901B7 9A contactor |  |
| Relay | Switching device used to control lower-power devices | Finder 38.51 EMR interface module |  |
| Inverter | Device used to control the speed of electric motors by adjusting the supply frequency | Lenze i510 servo drive |  |
| Small solenoid valve | Device used to control the flow of media (often water or air) in pipelines | Festo VUVS solenoid valve |  |
Transistor Outputs of the S7-1200 PLC
Characteristics of Transistor Outputs
- Type: Use transistors to switch loads. These can be MOSFET transistors or open-collector bipolar transistors.
- Voltage: Typically operate within a voltage range of 24V DC.
- Current: They can supply low current, usually 0.5A to 2A.
Advantages of Transistor Outputs
- Speed: Transistor outputs operate faster than relay outputs.
- Durability: They have no moving parts, resulting in longer lifespan.
Disadvantages of Transistor Outputs
- Limited current: Not designed for switching heavy loads.
- Sensitivity: They may be more susceptible to damage from voltage spikes than relay outputs.

Relay Outputs of the S7-1200 PLC


Characteristics of Relay Outputs
- Type: Use electromagnetic relays to switch loads.
- Voltage: Can operate with various voltages, both AC and DC.
- Current: Depending on the relay type, they can switch significant loads, often up to several amps.
Advantages of Relay Outputs
- Flexibility: They can switch various voltages and types of loads.
- Isolation: Provide good isolation between the PLC and the load.
Disadvantages of Relay Outputs
- Speed: Operate slower than transistor outputs.
- Lifespan: Have moving parts, which may lead to a shorter lifespan compared to transistor outputs, especially in applications with frequent switching.

Choosing the Right Type of Outputs in the PLC
The choice between transistor and relay outputs depends on the specific application:
- If you need to switch quickly and frequently, transistor outputs may be a better choice.
- If you need to switch different voltages, especially AC, or heavy loads, relay outputs may be more appropriate.

It is therefore recommended to use controllers with transistor outputs and intermediate power supply to actuators that draw more current, e.g., via interface relays or contactors.

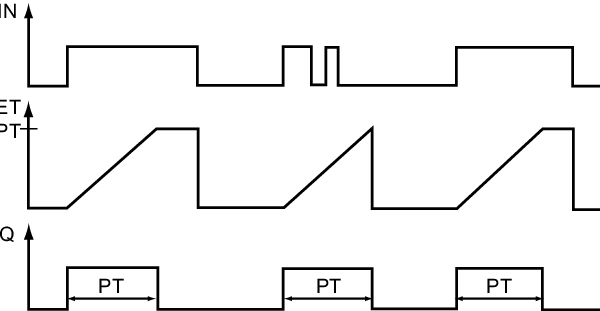
High-Speed Outputs (PTO) of the S7-1200 PLC
Like high-speed inputs, high-speed outputs are designed to generate high-frequency signals.
Applications of High-Speed Outputs
- Drive Control: Generating PTO pulses to control stepper motor and servo motor amplifiers
- Generating PWM Signals (Pulse Width Modulation): To control motor speed, light brightness, etc.
Characteristics of High-Speed Outputs
- High Frequency: Can generate signals at frequencies of tens of kHz.
- Precise Timing: Allow for accurate control of signal duration and frequency.

Siemens S7-1200 PLC Tutorial Outline: