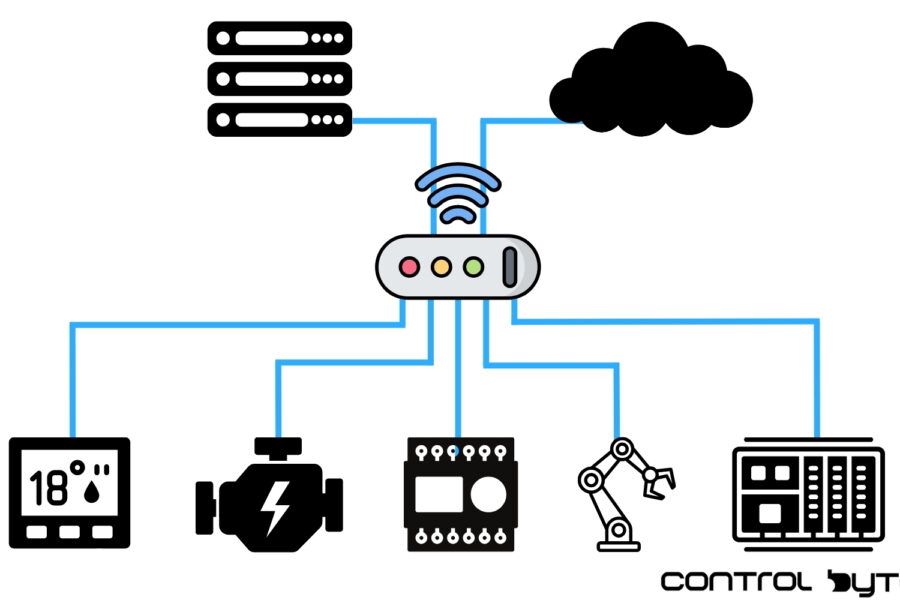
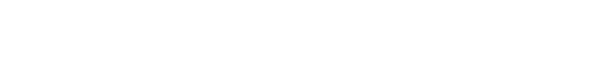Introduction to IIoT and Industry 4.0
Data has increasingly become a valuable asset, propelling industries through a digital transformation aimed at optimizing operational efficiency and connectivity. Central to this movement is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), an essential element of Industry 4.0 that brings a powerful technological advancement to industrial practices. This article explores the realm of IIoT, examining its fundamental concepts, differentiating it from the general Internet of Things (IoT), and showcasing its practical applications that are innovating various industries.
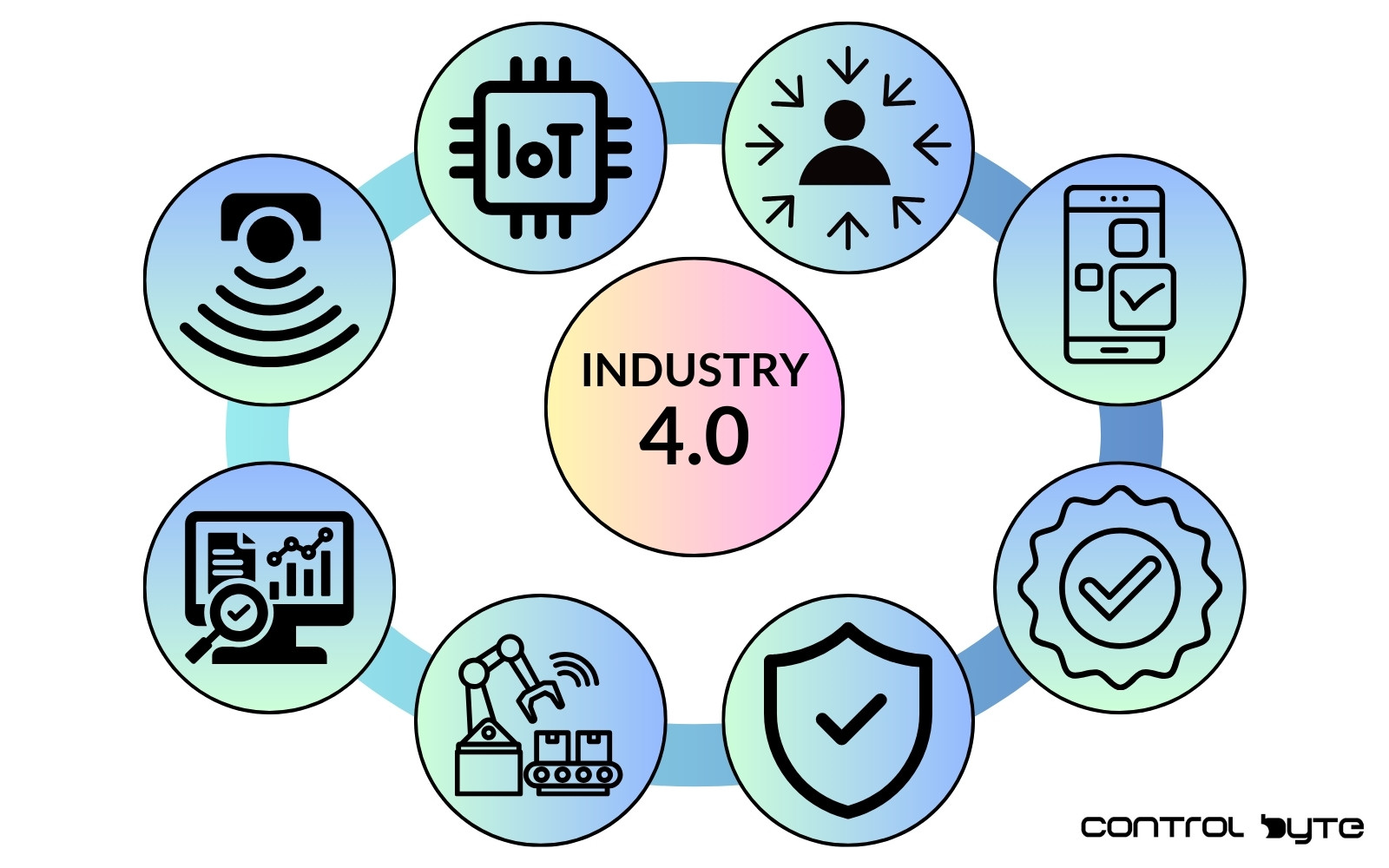
Understanding the Basics: IIoT vs. IoT
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) signifies the extension of IoT into industrial environments. It focuses on seamless machine-to-machine communication, big data analytics, and machine learning, empowering businesses to boost their operational effectiveness. IIoT spans across industries and includes robotics, medical equipment, and sophisticated production processes.
IIoT uniquely combines information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT). OT includes systems managing operational processes, such as supervisory control, SCADA, and DCS systems. By merging these technologies, IIoT fundamentally transforms industrial operations, supporting data-driven decision-making.
IIoT vs. IoT: Key Differences and Overlaps
IoT comprises a vast network of physical devices known as “things,” equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to interact with other devices and systems. From household gadgets to smart city applications, IoT is part of daily life, with over 15 billion IoT devices in use worldwide.
IIoT vs. IoT: Key Differences
The primary distinction between IoT and IIoT is their purpose. While IoT is often focused on consumer applications for convenience, IIoT aims at enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial settings.
| Aspect | IIoT (Industrial IoT) | IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Large-scale networks | Smaller-scale networks |
| Connectivity | Both wired and wireless | Primarily wireless |
| Data Quantity | High to very high | Medium to high |
| Interoperability | Integrates with diverse technologies | Primarily independent |
| Sensor Utilization | Advanced sensors (e.g., torque, RFID) | Basic sensors (e.g., motion, temp) |
| Cybersecurity | Advanced protocols | Moderate protocols |
| Objective | Automation, safety, efficiency | User convenience |
Similarities Between IIoT and IoT
Both IIoT and IoT share foundational principles: device connectivity, cloud computing, machine learning, and AI for smart decision-making. They leverage common devices like sensors and cameras, prioritize energy efficiency, emphasize security, and support scalable system expansion.
How Does IIoT Work? Understanding Core Components
IIoT connects smart devices into systems for data gathering, communication, and analysis:
- Connected Devices: These devices capture and share information.
- Data Communication: Networks transmit data from devices.
- Analytics and Applications: Data processing offers actionable insights.
- Data Storage: Data is stored for future analysis.
- Human Interaction: Information aids in decision-making.
These interconnected devices help maintain machinery, manage processes, and inform predictive maintenance strategies, optimizing business operations.
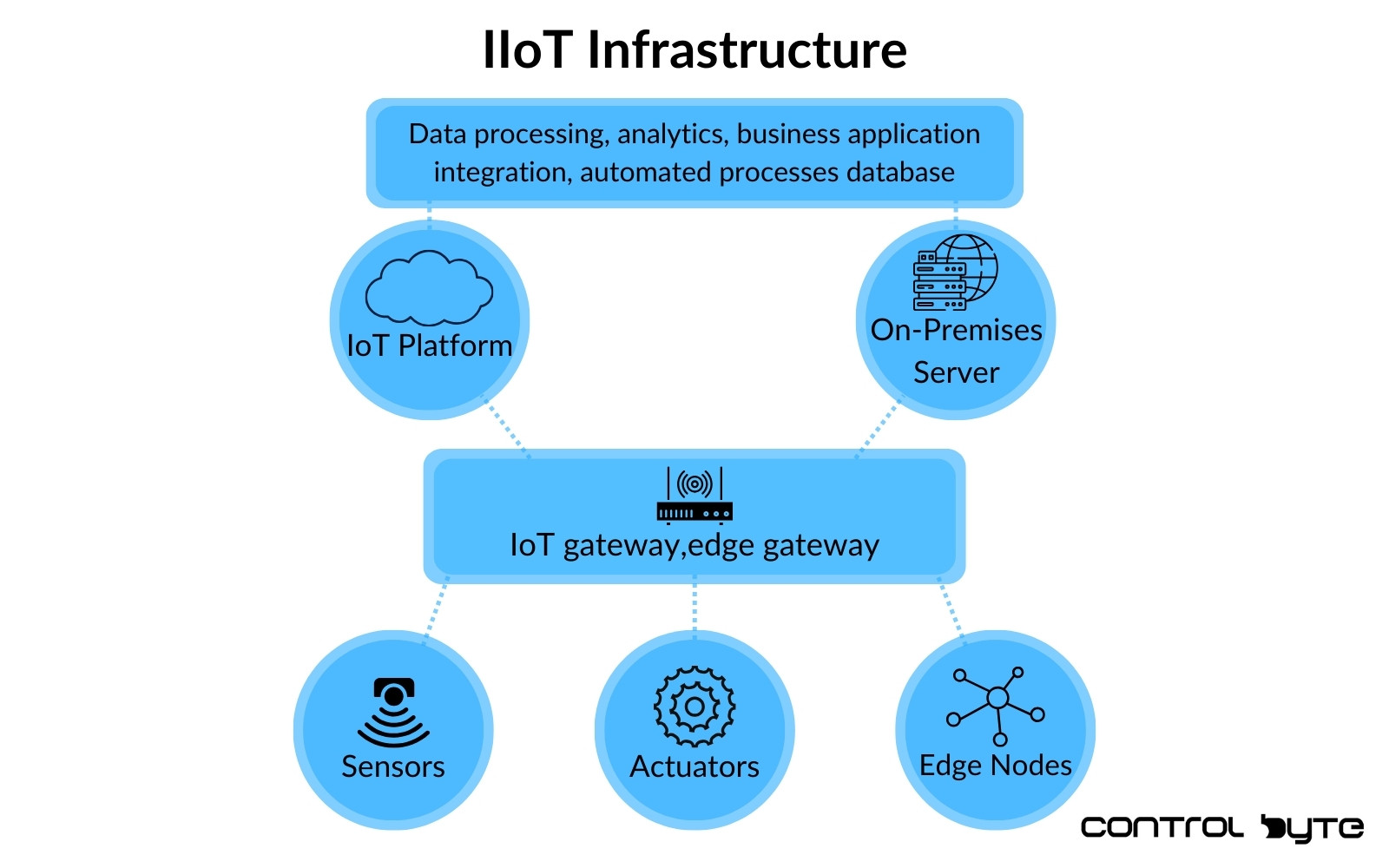
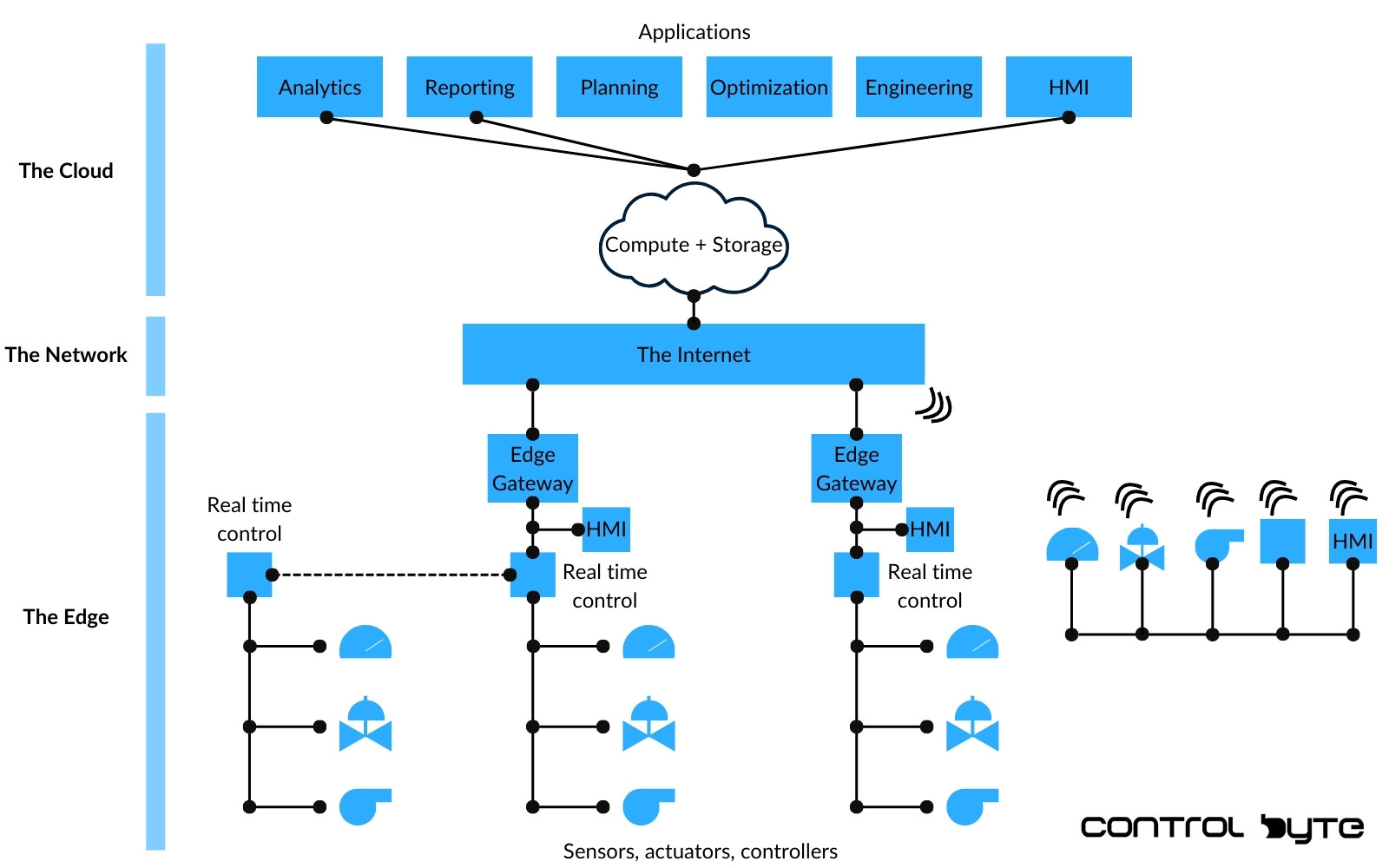
Exploring IIoT Architecture: Edge, Network, and Cloud Layers
IIoT architecture typically includes:
- Edge Layer: Sensors and controllers gather and initially process data.
- Network Layer: This layer transfers data to cloud systems.
- Cloud Layer: Comprehensive data analysis, incorporating advanced analytics and AI.
This architecture enables immediate data responses at the edge while facilitating deeper analysis in the cloud.
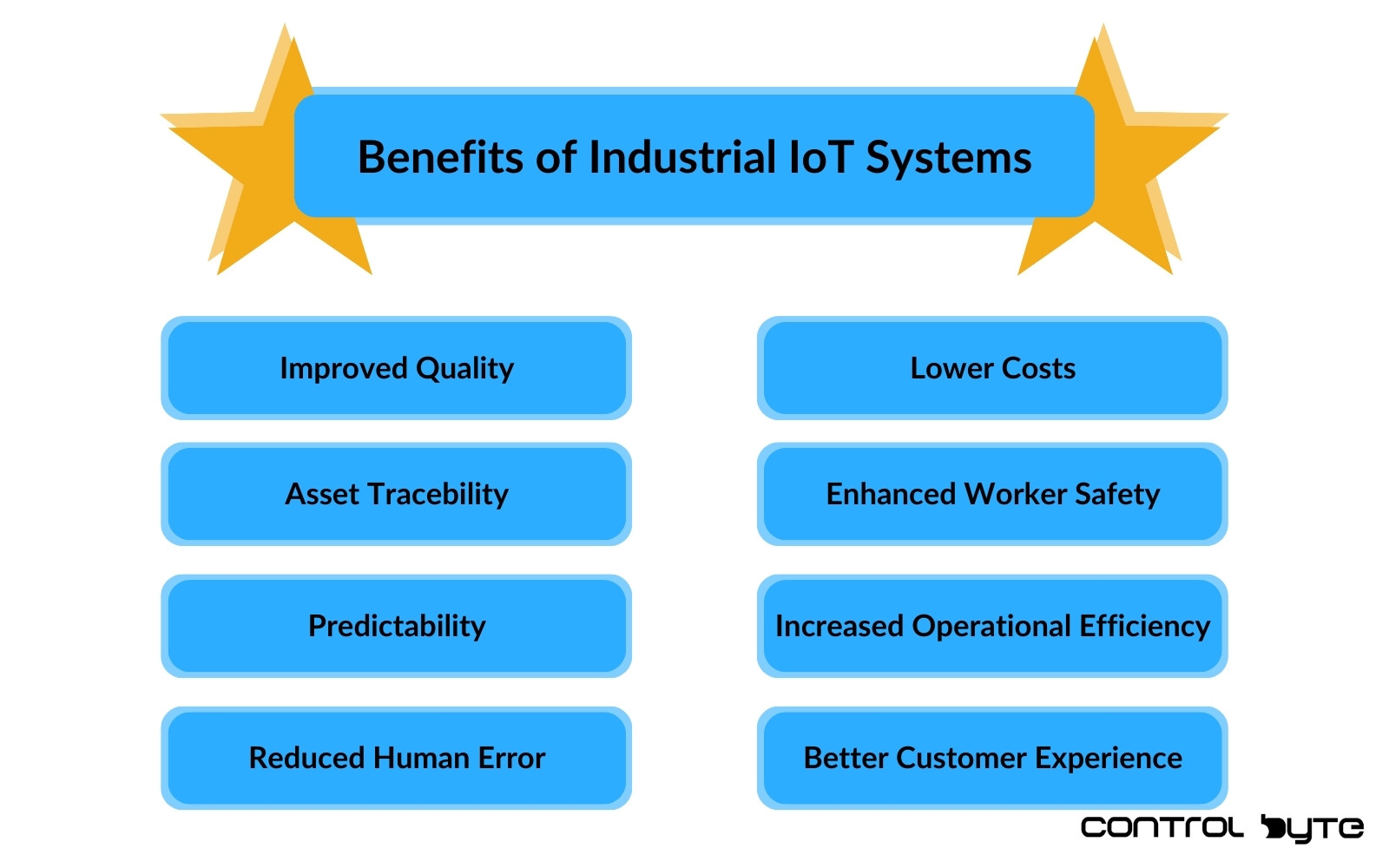
How IIoT Drives Efficiency and Productivity
IIoT delivers multiple business benefits, including:
- Efficiency Gains: Real-time monitoring allows automation and better decision-making.
- Increased Production: Streamlined equipment performance boosts capacity.
- Reduced Errors: Automation reduces product defects, improving quality.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors enable preemptive maintenance, minimizing downtime.
- Enhanced Safety: Sensors monitor workplace safety.
- Energy Savings: Monitoring and optimizing energy consumption lowers costs.
- Improved Customer Service: Real-time data enhances customer support.
Industrial IoT Security: Ensuring Safety and Reliability
IIoT security is vital given its extensive interconnectivity and data generation. To mitigate risks, companies use data encryption, access controls, device authentication, and network segmentation. Monitoring IIoT networks and adhering to industry standards helps secure sensitive data.
Addressing the Challenges of IIoT Implementation
Challenges in IIoT include:
- System Integration: Integrating IIoT with existing systems requires sophisticated solutions.
- Data Management: Handling large data volumes calls for efficient storage and analysis tools.
- Skills Gap: Demand for IIoT experts exceeds supply.
- Interoperability: Compatibility between diverse devices is challenging.
- Scalability: Expanding IIoT networks requires robust infrastructure.
- Bandwidth: Sufficient bandwidth is needed for seamless device communication.
The Transformation of Industries with Industrial IoT Applications
IIoT adoption is broadening, with applications across various sectors:
- Logistics: Drone technology aids rapid deliveries.
- Manufacturing: Real-time insights improve production.
- Agriculture: Automated tractors enhance efficiency.
- Automotive: Sensors optimize autonomous vehicle navigation.
- Construction: Equipment tracking improves safety and compliance.
- Power: IIoT simplifies power grid management.
- Cybersecurity: IIoT enhances endpoint monitoring.
Key Applications and Use Cases of IIoT Across Industries
- Fanuc: IIoT sensors for predictive maintenance.
- Airbus: Smart factories with safety-focused IIoT tools.
- Maersk: Route optimization for shipping.
- John Deere: Self-driving agricultural equipment.
Key IIoT Vendors and Solutions in the Marketplace
Notable IIoT vendors include ABB, Cisco, GE, Siemens, and Microsoft Azure, each offering innovative solutions that help industries harness the power of IIoT for optimized performance.
Examples of such devices:
RevPi Aio
Description: The RevPi Aio, an innovative IIoT device, is engineered for applications that demand robust connectivity, data acquisition, and practical efficiency within industrial environments. Designed for flexibility and modular expansion, this device supports diverse industrial applications by integrating various sensors, controllers, and cloud connectivity options. As part of the broader Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem, RevPi Aio offers powerful solutions for automating industrial processes, driving digital transformation, and improving real-time data handling. This IIoT solution supports modern cloud computing and edge devices, enabling advanced data analysis and machine learning models to run closer to the data source, which is essential for efficient industrial operations.
Example Application: In an industrial manufacturing environment, RevPi Aio can be deployed as part of an IIoT network to optimize practical processes. Connected to the internet, it enables predictive maintenance by monitoring equipment conditions and identifying patterns of wear. Through its IIoT architecture, RevPi Aio can streamline practical processes by identifying equipment malfunctions in real-time and automatically triggering alerts or maintenance actions. This solution is particularly valuable for industries aiming to reduce downtime and increase the lifespan of their equipment, benefiting from the digital industrial applications central to Industry 4.0.

Finder Opta
Description: Finder Opta is a compact, programmable logic controller (PLC) specifically designed to enhance industrial IoT (IIoT) applications. It is widely used in industry for its ability to support small- to medium-scale automation tasks, enabling companies to automate operational processes effectively. Its compatibility with IIoT technologies allows it to seamlessly integrate within an IoT ecosystem, making it ideal for managing industrial infrastructures that require remote monitoring, real-time data analysis, and process optimization. Finder Opta is connected to smart devices and sensors that provide industrial data, enhancing the system’s ability to optimize resources and streamline production, essential for digital transformation.
Example Application: In building automation within an industrial setting, Finder Opta serves as a critical device for optimizing energy usage. By connecting with sensors and smart devices, it automates HVAC and lighting systems, responding dynamically to factors like occupancy and external temperature. Through cloud computing integration, Finder Opta provides insights on energy consumption and operational efficiency, enabling buildings to cut costs while reducing their environmental impact. This IIoT deployment supports Industry 4.0 goals, where energy-efficient, connected environments represent a key element of the fourth industrial revolution.
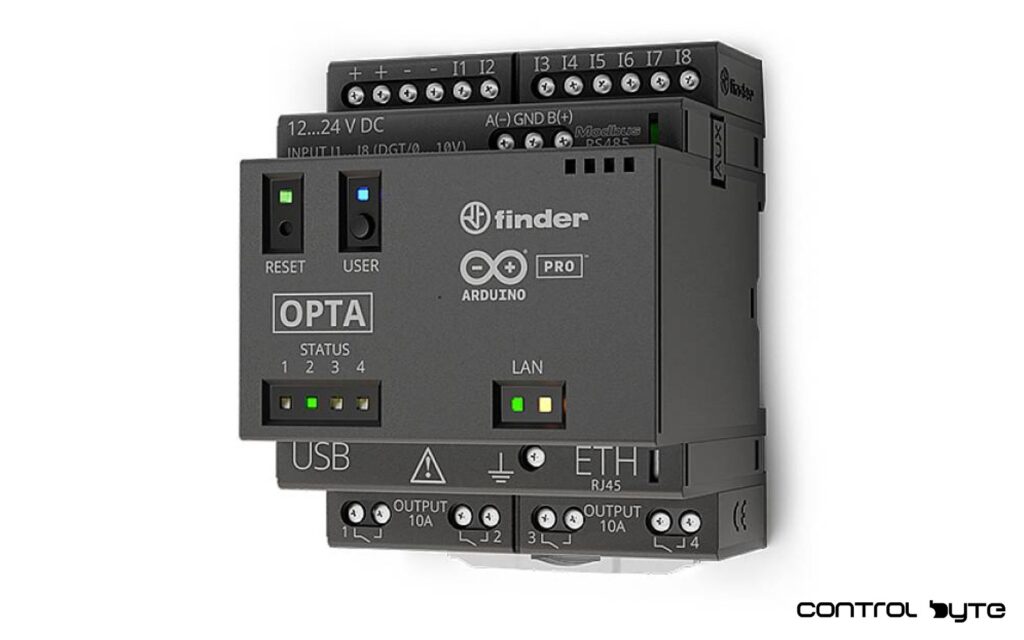

SIMATIC IOT 2000
Description: The SIMATIC IOT 2000 by Siemens is a versatile IIoT gateway that facilitates seamless data communication and interoperability between legacy industrial equipment and modern IIoT systems. Engineered for complex industrial environments, SIMATIC IOT 2000 supports IIoT adoption by connecting devices to the internet, providing secure data transfer, and enabling data-driven decision-making. It serves as a bridge within IIoT architecture, transferring data from edge devices to cloud infrastructure, thereby streamlining industrial processes and enhancing the IIoT ecosystem. With its secure design and compliance with industrial IoT security standards, SIMATIC IOT 2000 is a reliable IIoT device that addresses security risks, making it integral for modern industrial operations and IIoT implementations.
Example Application: In the logistics and supply chain industry, SIMATIC IOT 2000 is used to track shipments, monitor inventory, and optimize distribution networks. By connecting to sensors on transportation vehicles and storage units, it collects data on conditions such as temperature and humidity, which are crucial for transporting perishable goods. The device then securely transmits this data to a centralized system for analysis, enabling companies to automate processes, reduce spoilage, and enhance supply chain efficiency. As a key IIoT solution, SIMATIC IOT 2000 drives digital transformation across supply chains, embodying Industry 4.0’s focus on optimized connectivity and operational efficiency.

The Future of industrial internet of things and Digital Innovation
Looking ahead, IIoT promises advancements in:
- Automation: Enhanced automation to reduce manual tasks.
- 5G and Connectivity: Faster data exchange with minimal latency.
- Edge Computing: Real-time data processing near the source.
- AI Integration: Improved data analysis and predictive maintenance.
- Interoperability: Standardization efforts for seamless integration.
- Sustainability: IIoT for efficient resource management.
Leveraging IIoT for a More Efficient and Secure Industrial Landscape
The Industrial Internet of Things stands as a transformative force within Industry 4.0, revolutionizing the way industries operate. By integrating IT with OT, IIoT emphasizes safety, efficiency, and sustainability in industrial environments, paving the way for smarter, connected systems. Despite implementation challenges, advancements in IIoT promise improved processes, reduced costs, and significant industrial innovation, foreshadowing a more connected and efficient future.
Thank you for reading! If you’re interested in learning more, explore our courses for in-depth training: Control Byte Courses.