In my first job, I was given a task
“Hey, Junior… get us a 24V power supply for the new project ASAP!”
In my first job, my boss asked me to select a power supply for a new project. Confidently, I thought, ‘No problem!’ After all, circuit theory and switching power supply design were things I knew well from school. I jumped onto an automation components website and found two options: a 24VDC 5A power supply for $12 and another 24VDC 5A power supply for $75—almost identical on the outside!
I wondered… The more expensive one must be better, right? But would the cheaper one suffice? What if my boss questions my choice? Wouldn’t it be safer to go with the more expensive one? But then again, if I choose the cheaper one and the machine breaks down, who’ll be flying to Mexico for repairs?
Don’t get stuck guessing. Instead, check out the following guide.
Why Use 24VDC in Control Systems?
- Safety: 24VDC is considered a safe low voltage, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock while being high enough to efficiently power and control devices.
- Interference Resistance: 24VDC is less susceptible to external interference than lower voltages like 5VDC or 12VDC, providing better signal stability in industrial environments with potential disturbances.
- Range and Distribution: It allows for longer transmission distances without significant voltage drops compared to lower voltages.
- Standardization: Over time, 24VDC has become an industry standard for many control applications, making component exchange, integration, and maintenance simpler.
- Compatibility: Many control device manufacturers offer 24VDC-compatible products, making it a practical choice for system integrators.
- Versatile Applications: 24VDC is suitable for various devices, from simple sensors to more complex controllers like PLCs, making it a universal choice for many control applications.
- Flexibility: 24VDC systems can be powered by both batteries and network power supplies, offering flexibility in system design and configuration.
Was 24VDC Always Used in Automation?
No, 24VDC wasn’t always the standard in control systems. Over the years, different voltages were used across applications and industries based on the available technology and specific system needs. Historically, control transformers provided voltages such as 110VAC or 220VAC, before low-voltage power supplies became more widespread. As technology advanced, understanding the risks associated with higher voltages and the push to reduce electrical hazards led to a shift toward low-voltage control systems, like 24VDC. Moreover, improvements in semiconductor technology and miniaturization allowed for more compact and efficient low-voltage power supplies. As the industry recognized the benefits of lower voltages, such as enhanced safety and reduced interference, 24VDC became more prevalent in control circuits.

Methods for Powering Machine Control Circuits
The IEC 60204-1 standard covers the electrical equipment of machines and includes guidelines on powering control circuits. Here are some common methods of powering control circuits according to the standard:
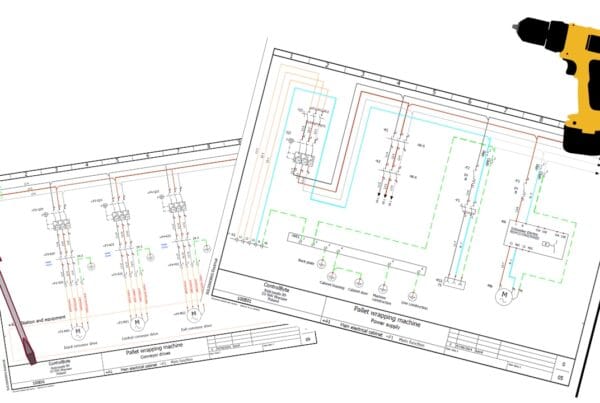
Directly from the Network:
In this method, control circuits are powered directly from the electrical grid. Although simple, this method may not be suitable for all applications, particularly where there’s a risk of electric shock or where lower voltages are required. For safety, circuits powered directly from the grid often include appropriate protections, such as overload switches or fuses. Commonly used in simpler systems where a single motor is controlled.
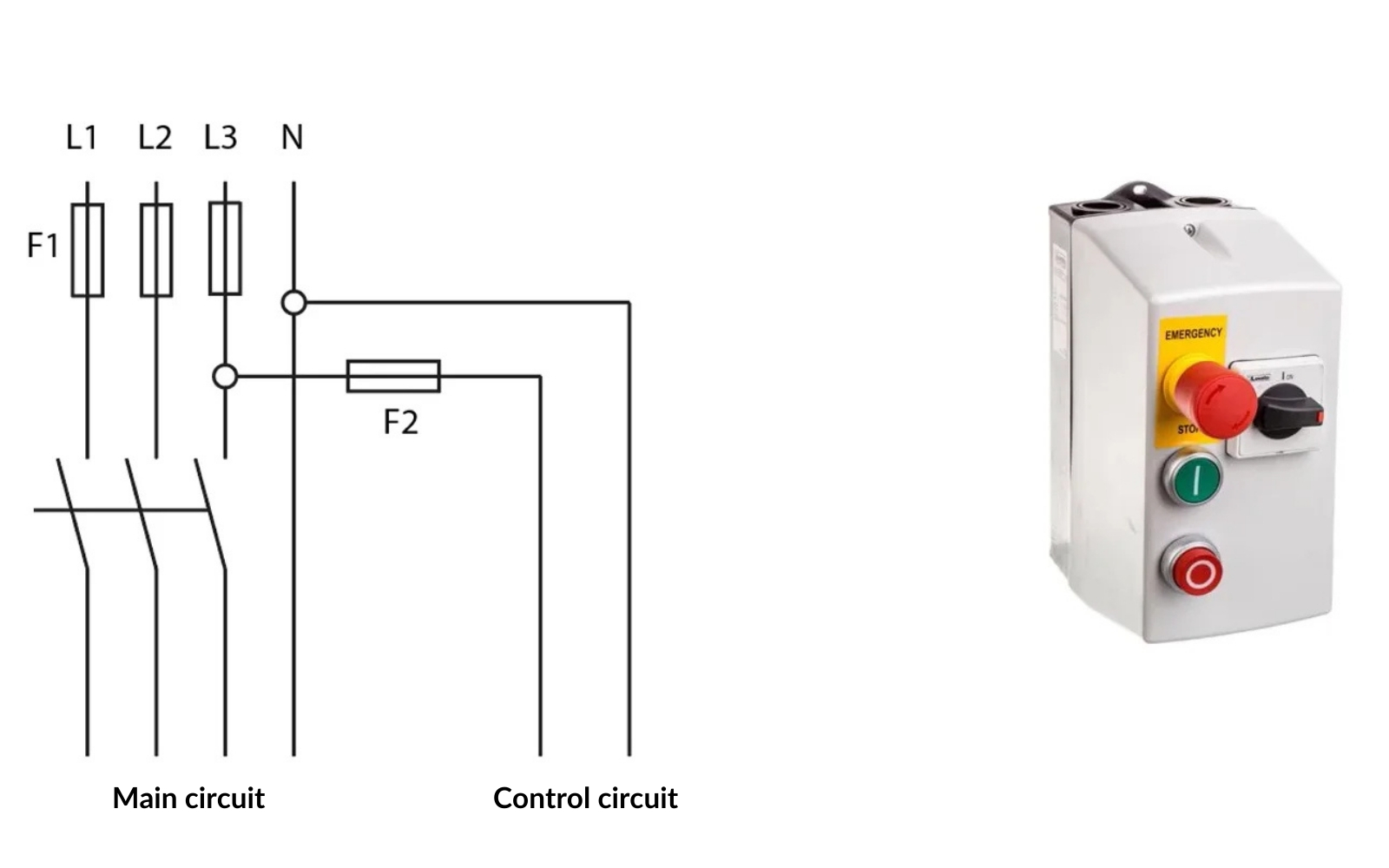
Using a Control Transformer:
A control transformer is used to convert the grid voltage to a lower voltage, more suitable for control circuits. This approach enhances safety, as the lower voltage (e.g., 24VAC) is less hazardous. The control transformer can also provide galvanic isolation between the network and the control circuit, which is beneficial for shielding against interference and surges.
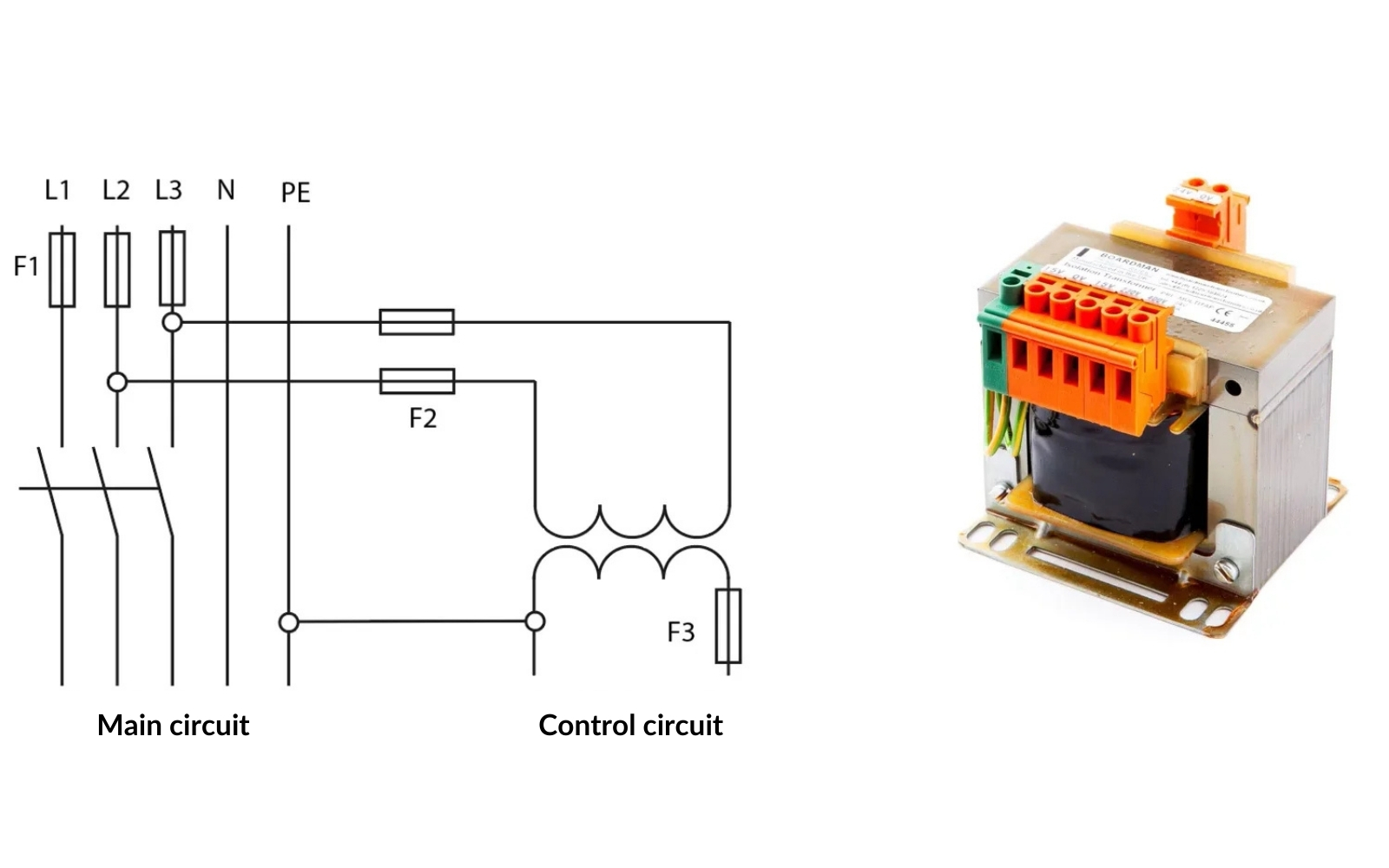
Using a Switching Power Supply:
Switching power supplies, also known as AC/DC converters, are used to convert AC voltage to DC, commonly used in modern control circuits. With a switching power supply, you can obtain stable and regulated DC voltage, such as 24VDC, which is widely used in industrial settings. These power supplies are efficient, compact, and often offer overload protection as well as dust- and water-resistant designs.
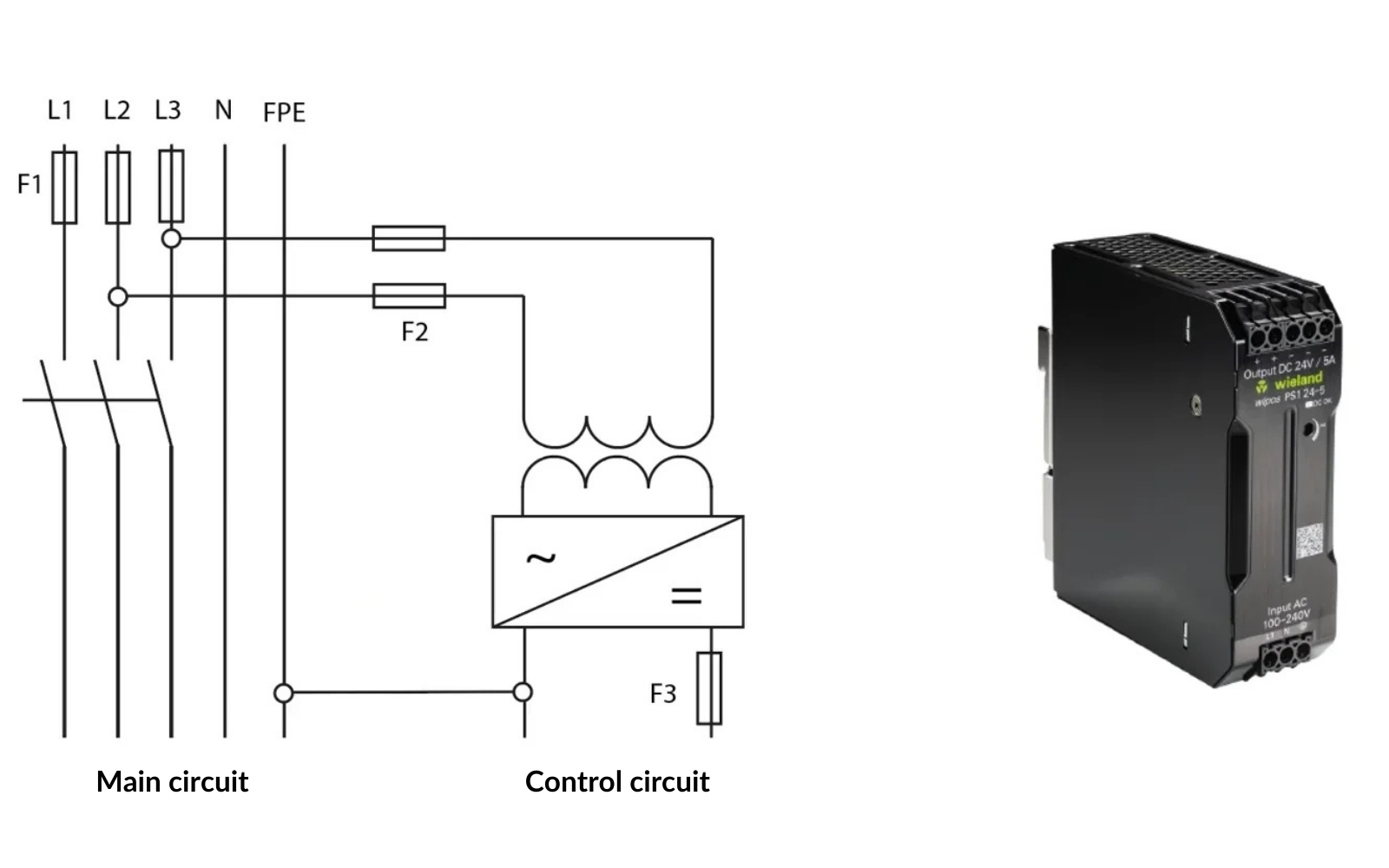
The IEC 60204-1 standard addresses the safety of electrical machines and is widely applied in the industry to ensure that machines are safe for operators and compliant with international requirements. One aspect of this standard is selecting a 24VDC power supply. The standard sets requirements for selecting, installing, and protecting these power supplies to ensure reliability and safety. Requirements include overload protection, wire protection, proper grounding, and short-circuit and surge protection. Choosing an appropriate 24VDC power supply in line with IEC 60204-1 ensures that a machine operates reliably and safely under various conditions.
What Makes a 5A 24VDC Power Supply Cost $12 or $75?
You’ll find 24VDC power supplies on the market for various applications, such as LED lighting, surveillance systems, IT and computing applications, fire protection systems, industrial automation systems, and machine control systems. The price range for similar-rated power supplies is vast!
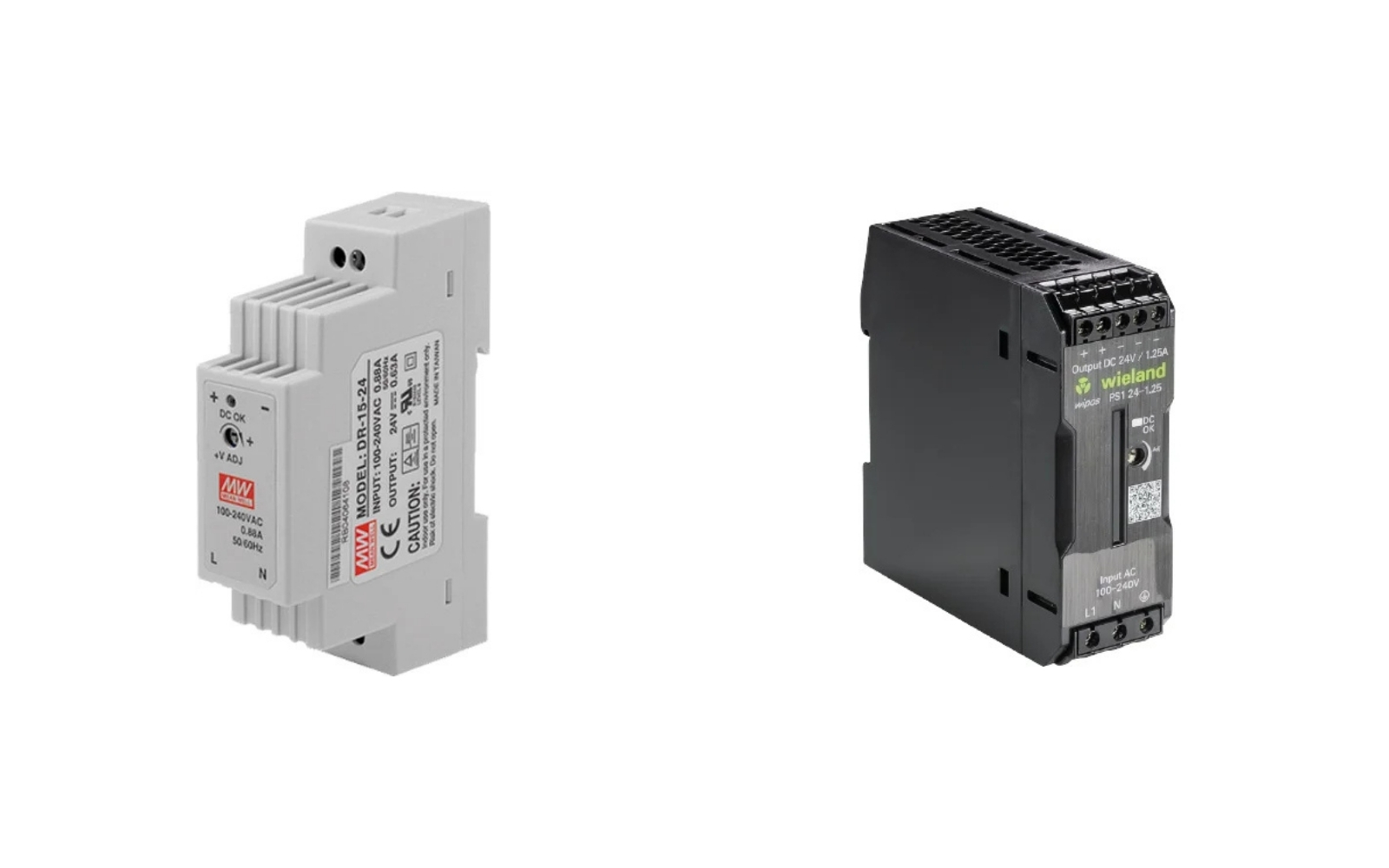

Why the Difference? And Which Power Supply to Choose for Machine Control?
IEC 60204-1 requires measures that reduce the likelihood of unintentional machine startup, potentially dangerous movements, and inability to stop the machine. The IEC 60204-1 standard recommends using a PELV (Protective Extra-Low Voltage) system or an insulation monitoring device (see an example of an EMR relay here) as one way to mitigate the effects of short circuits in control circuits. To meet PELV requirements, a switching power supply must have proper isolation between the primary and secondary sides!
PELV System for a Machine Power Supply Circuit
PELV power supplies are designed to provide adequate isolation, which is key to protecting against electric shock. They are equipped with several essential features:
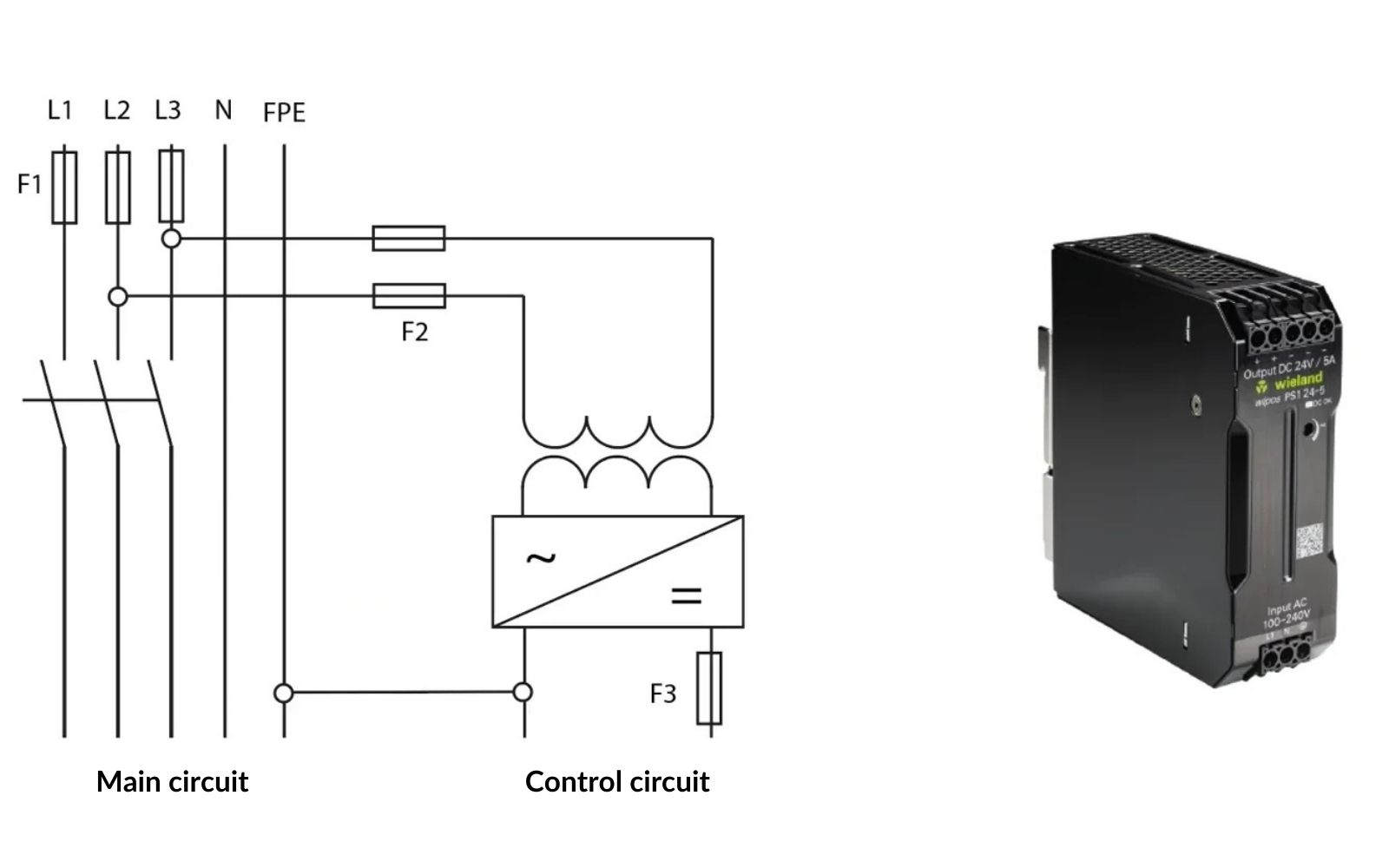
- Transformer with Safe Isolation: PELV power supplies often use transformers with safe isolation, designed to ensure both physical and electrical separation between the primary and secondary windings.
- Reinforced Insulation: These power supplies use reinforced insulation with a thicker insulation layer, offering greater resistance to breakdowns than standard insulation. Reinforced insulation provides a higher safety margin.
Cheaper power supplies may not meet these requirements, and in case of failure, the secondary side can experience high voltages (230/400V), posing serious risks.
| Description | Standard |
|---|---|
| Normative equipment of electronic devices in electronic technical means | EN 50178/VDE 0160 (PELV) |
| Normative limitation of higher harmonics of network current | EN 61000-3-2 |
| Normative electrical safety | EN 60950-1/VDE 0805 (SELV) |
| Normative protection against health-hazardous current, basic requirements for safe separation in electronic equipment | EN 50178 |
| Normative protective low voltage | EN 60950-1 (SELV) |
| EN 60204 (PELV) | EN 60204 (PELV) |
| Normative secure separation | DIN VDE 0100-410 |
Steps to Choosing a 24V DC Power Supply
Now that you know what’s required by standards to design a safe machine, let’s focus on the technical parameters to consider when choosing a power supply.
- Analyze Power Requirements: Assess the power needs of your automation system, including current and voltage requirements for components like PLCs, sensors, and relays. Make sure the power supply can handle all components. Common current ratings include: 2.5A, 5A, 10A, 20A, 40A.
- Power Supply Input Voltage: Check the input voltage available in your installation. The power supply should be compatible with this voltage. The typical input voltage is 230V AC, but it may also be 400V AC or another value.
- Power Supply Load Capacity: The power supply should handle the load of the automation system. Ensure the power supply has adequate current capacity and can deliver sufficient current for all connected components. Some power supplies offer a “boost” feature, temporarily increasing output to meet short-term demand spikes.
- Support for Protective Functions: Choose a power supply with built-in protections, such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, and overvoltage protection. These features protect the system from faults and potential damage due to improper operation.
- Physical Protection: Power supplies may be installed in various environments, from dry production halls to moisture- and dust-prone areas. Choose a power supply with appropriate protection ratings (e.g., IP20, IP65) to ensure durability and safety. Note that increased temperature in the control cabinet can reduce power supply efficiency!
Summary
Choosing the right 24V DC power supply for industrial automation systems is crucial for efficient and reliable machine operation. Analyzing power requirements, ensuring voltage compatibility, and considering protective features are key factors in selecting a power supply. Remember, selecting the correct power supply can significantly impact the performance and reliability of the entire automation system.