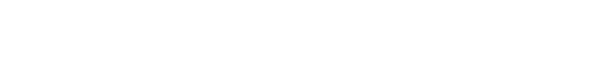Today, let’s take a closer look at each temperature sensor type, including RTDs, thermocouples, and thermistors. While these names might seem a bit technical, we’ll explain them in an approachable way!
RTDs: Precise platinum Temperature Sensors
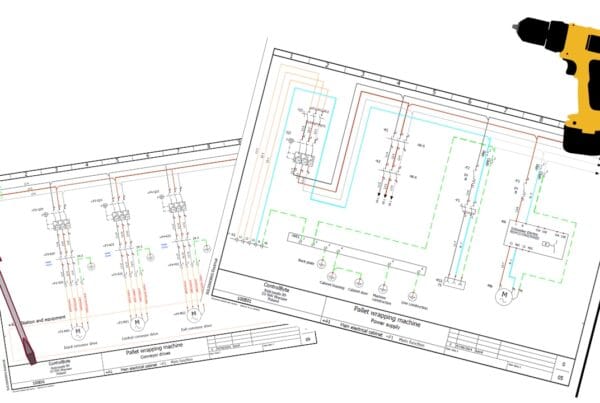
First on the list are RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors). These sensors measure temperature by detecting changes in electrical resistance within a wire. The process behind this is relatively simple. Imagine a platinum wire: as the temperature rises, the atoms in the metal vibrate more, which increases resistance to the flow of electricity, allowing for precise temperature readings.
RTDs take advantage of this principle by measuring the wire’s resistance to determine the surface temperature. It’s similar to how you can gauge heat by how long you can touch something hot. The more resistance, the hotter it is, which is a key principle in temperature measurement.
RTDs are known for their precision, able to measure temperature with an accuracy of 0.1% or better. It’s like hitting a target from far away and hitting it almost every time.
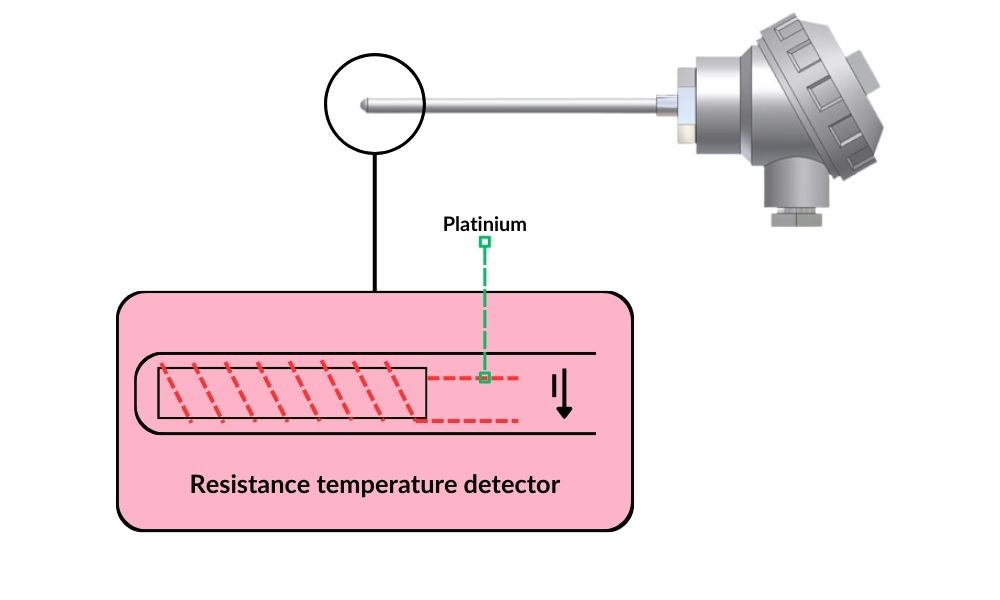
RTDs measuring sensors in Industrial Applications
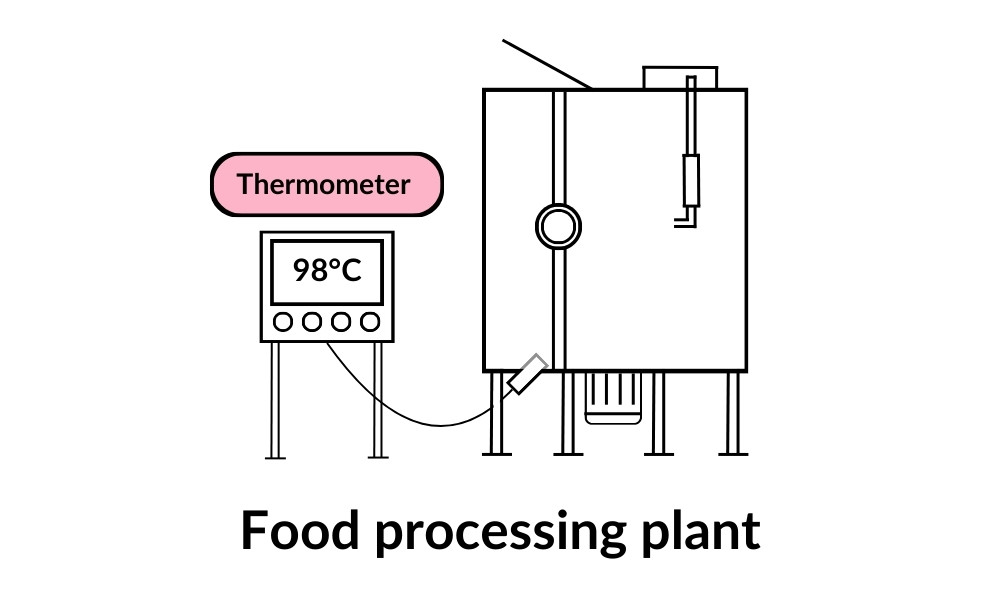
One common industrial use for RTDs is in food processing plants for reliable temperature readings. For instance, an RTD sensor might be installed in a thermometer placed inside a cooking vat to ensure accurate temperature readings. As the temperature of the food changes, the RTD detects this by measuring the resistance, sending the information to the thermometer, which then displays the temperature readings for workers to monitor.
This ensures that the food is cooked safely and at the right temperature, adhering to strict temperature measurement guidelines. RTDs may not sound like the most exciting piece of technology, but they’re essential for accuracy and safety in industries like these!
Thermocouples: Temperature Detection with Wires
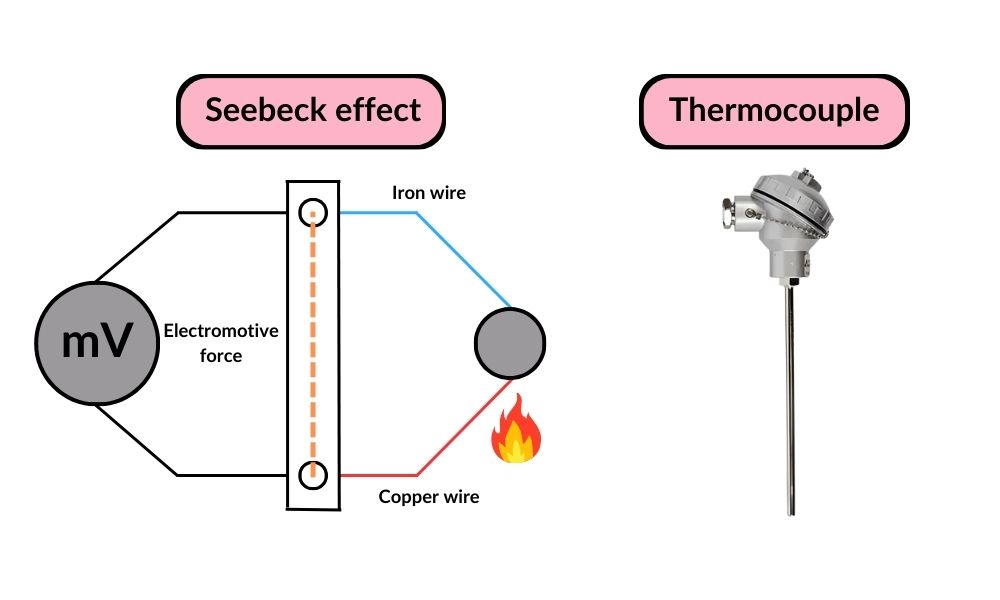
Next up are thermocouples, which operate using the Seebeck effect. This occurs when two different metals are joined to create a circuit. If you take a copper wire and an iron wire and heat one end, a small electrical current is generated due to the difference in temperature between the two ends. This creates an electromotive force (EMF), which is used to measure the temperature difference.
Thermocouples come in various types depending on the metals used. For example, Type K thermocouples use nickel and chromium, while Type J thermocouples combine iron and constantan, an alloy of copper and nickel. These devices can measure a broad temperature range, from -200°C to as high as 2000°C.as high as 2000°C.
Thermocouples in Industry: From Factories to Laboratories
Thermocouples are incredibly useful in industries that require extreme temperature control, such as factories producing ceramics, glass, or bricks, where precise temperature measurement is critical. These products need to be heated to very high temperatures, and thermocouples are essential in making sure the furnace temperature is monitored accurately for effective temperature measurement.
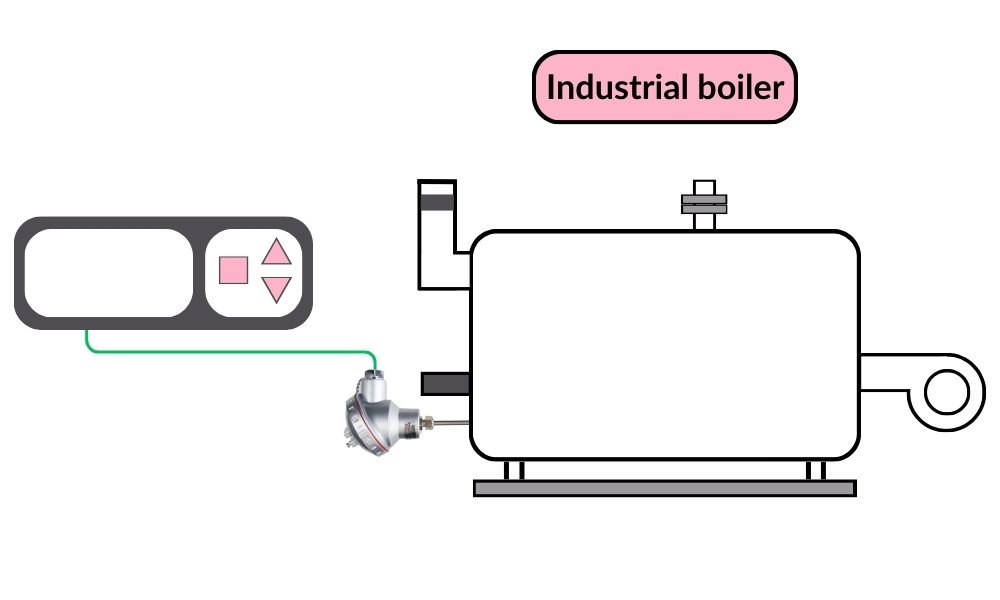
In addition, thermocouples are employed in boilers to prevent overheating and in scientific labs for measuring the temperature of materials and chemicals during experiments.
So, while they might seem complex at first, thermocouples are quite simple – they’re just wires generating electricity when heated, which can then be used to measure temperature.
Thermistors: The Resistance-Based Temperature Game
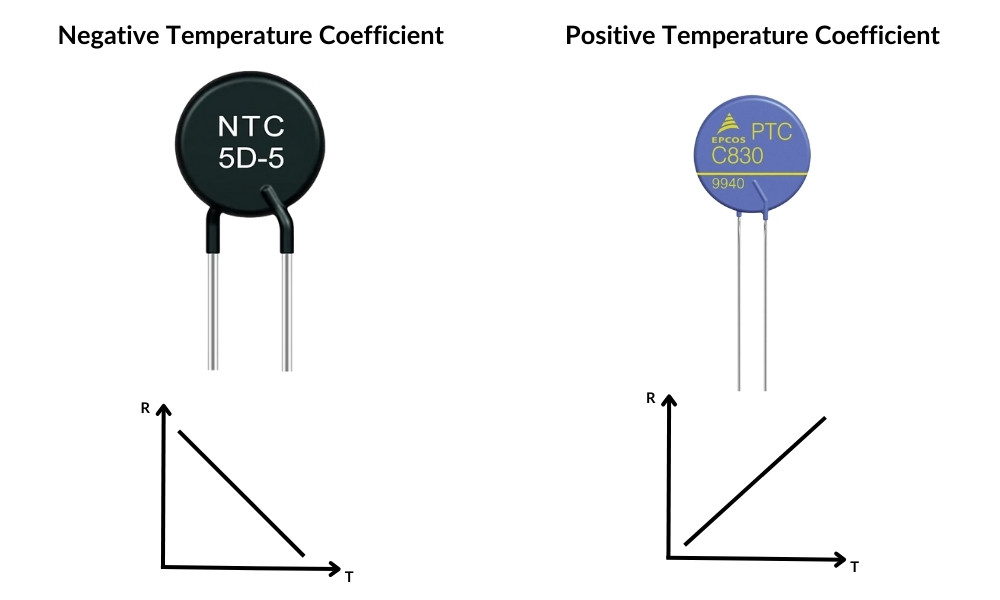
Finally, we have thermistors. These sensors detect temperature changes by monitoring how their resistance varies with temperature. There are two main types: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). NTC thermistors decrease in resistance as the temperature rises, while PTC thermistors increase their resistance as the temperature goes up.
Industrial Uses of Thermistors
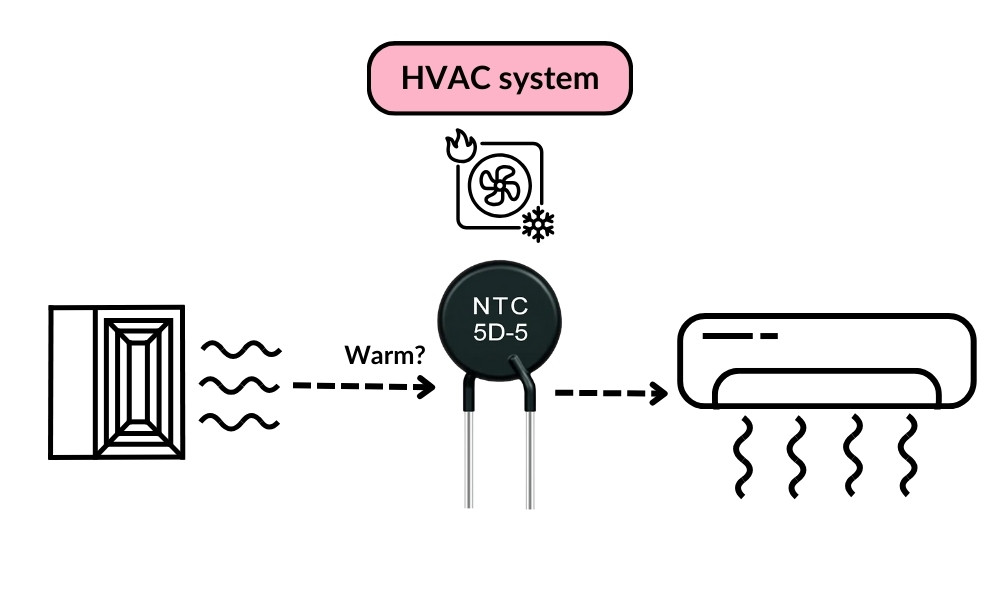
Thermistors are widely used in HVAC systems to ensure proper climate control. For example, in an air conditioning system, a thermistor monitors the air temperature coming from the vents. If it detects that the air isn’t cool enough, it signals the system to adjust accordingly.
Thermistors are also used in medical devices, such as thermometers, and in automotive engines to monitor temperature and prevent overheating.
Summary
In conclusion, temperature sensor technology might seem complex, but it plays a vital role in many industries. Today, we explored RTDs, thermocouples, and thermistors.
- RTDs, which use platinum wires to measure temperature, are commonly used in food processing for accurate temperature control.
- Thermocouples generate electricity when two metals are heated and can measure temperatures from extremely cold to incredibly hot, making them ideal for industrial applications like kilns and boilers.
- Thermistors, which change their resistance based on temperature, find use in various systems such as HVAC, medical equipment, and vehicle engines.
Thank you for reading! If you’re interested in learning more, explore our courses for in-depth training: Control Byte Courses.